今日概要:
- websocket & 聊天室的案例。
- websocket & gojs & 审批流的案例
- django核心的组件
1.websocket相关
请帮助我实现一个系统:20个用户同时打开网站,呈现出来的就是群聊。
- 我,你好
- 张坤
- 付乐乐
- 贾文龙
- ...
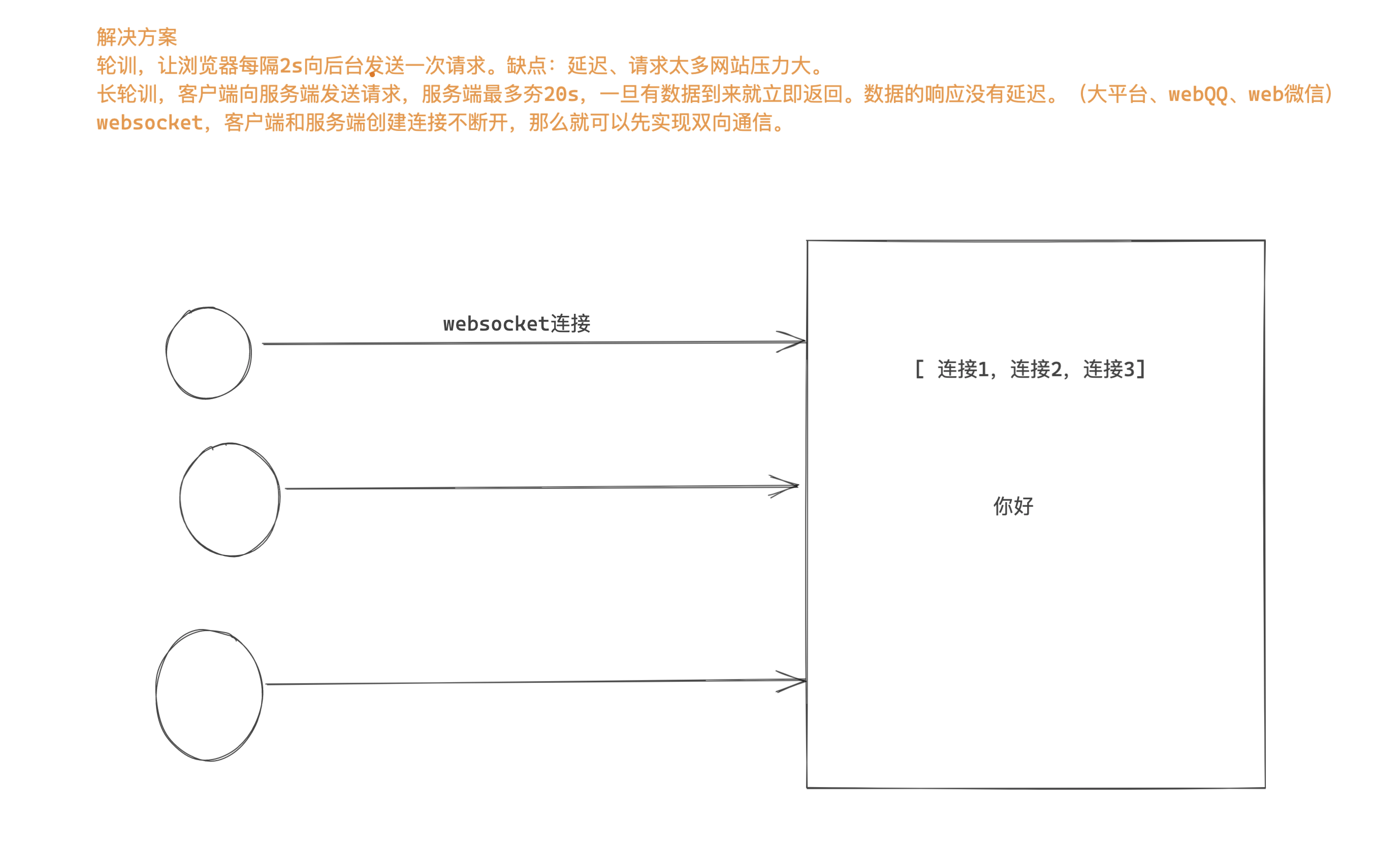
1.1 轮询
- 访问 /home/ 显示的聊天室界面。
- 点击发送内容,数据也可以发送到后台。
- 定时获取消息,然后再界面上展示。
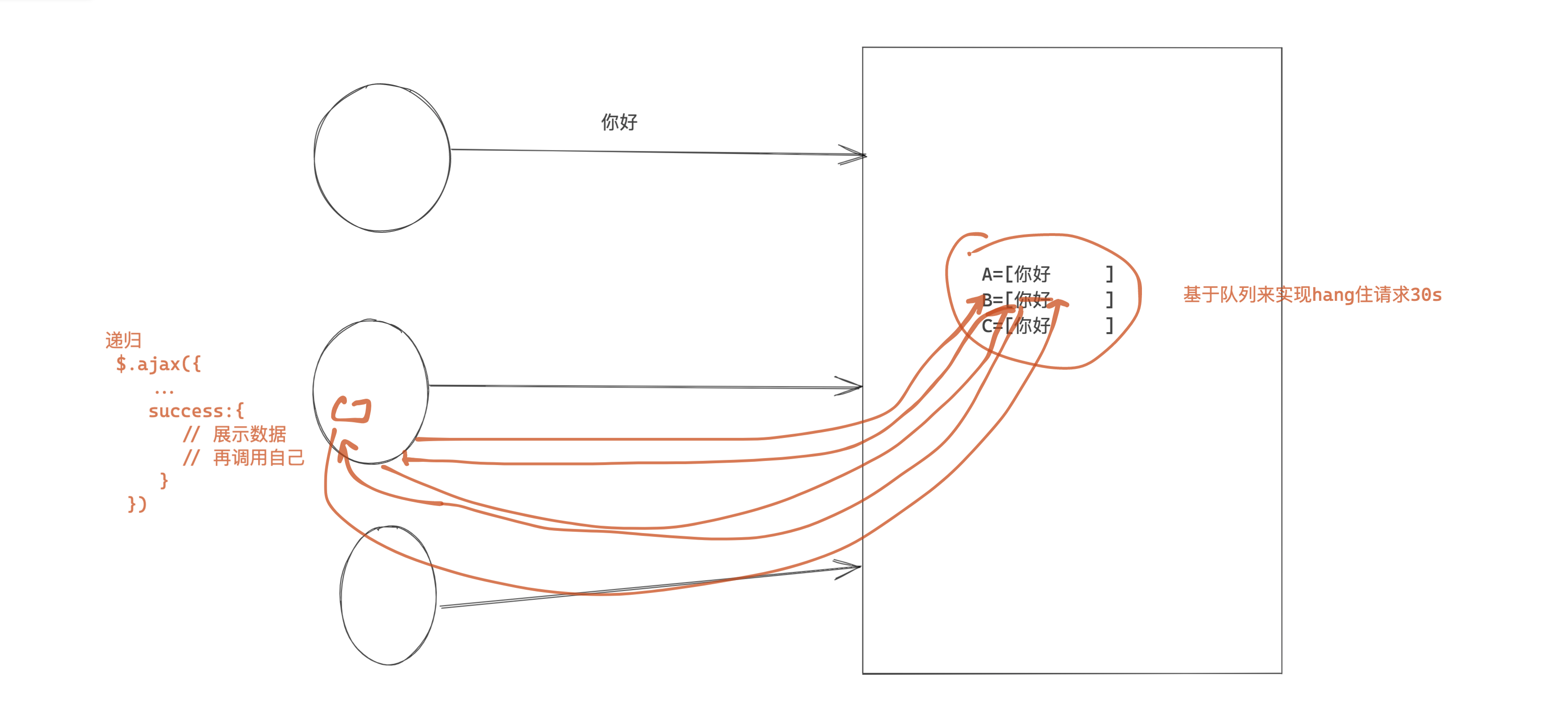
1.2 长轮询
- 访问 /home/ 显示的聊天室界面。 + 每个用户创建一个队列。
- 点击发送内容,数据也可以发送到后台。+ 扔到每个人的队列中
- 递归获取消息,去自己的队列中获取数据, 然后再界面上展示。
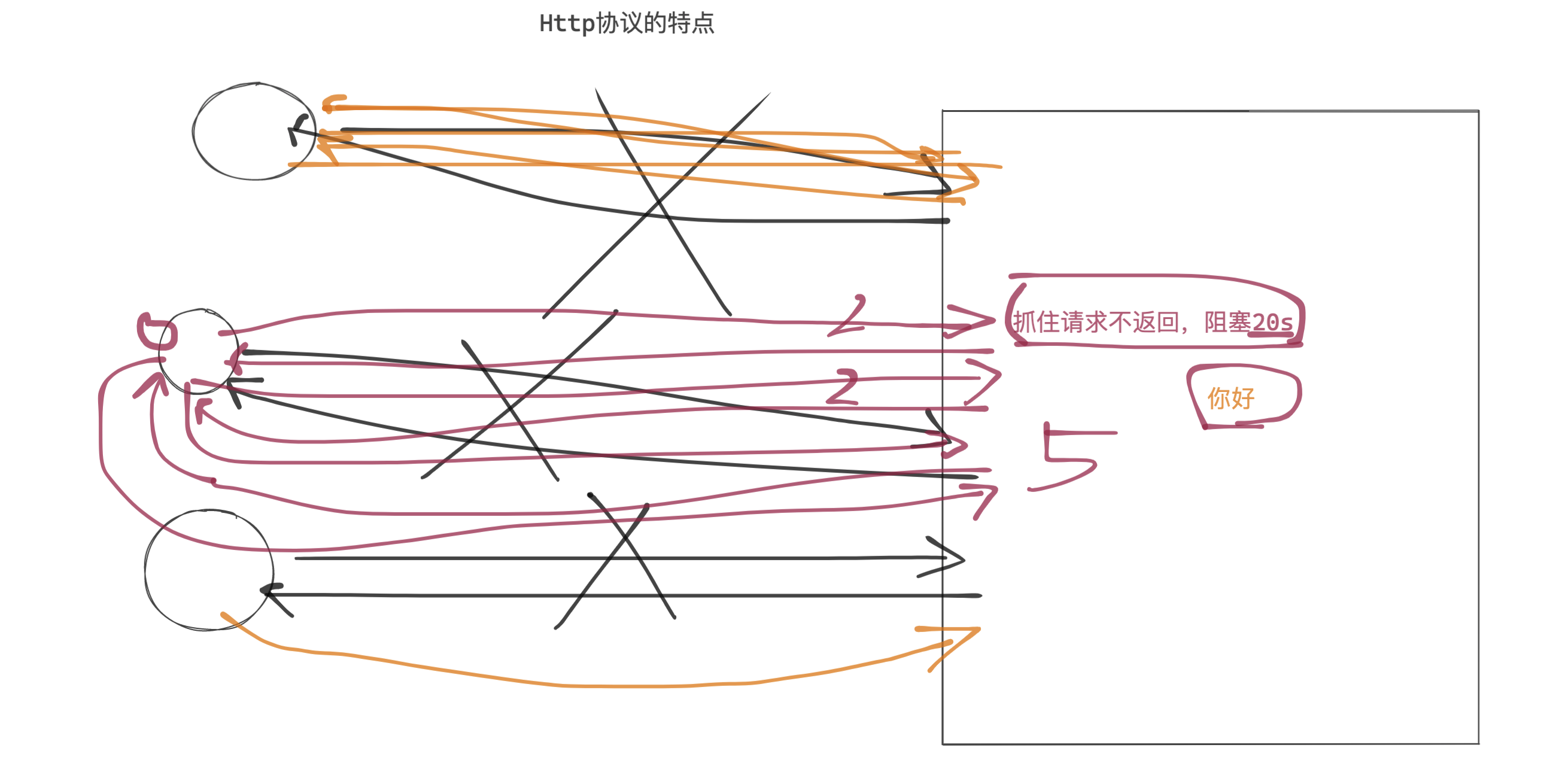
问题:
服务端持有这个连接,压力是否会很大?
如果即基于IO多复用 + 异步。100线程,同时100个用户的请求。(15分钟)
为什么一个用户一个队列。
示例:每个用户一个队列。
队列 A 队列 B 队列 Credis发布和订阅
A,1 发消息 [1] B,1 C,1
1.3 websocket
websocket,web版的 socket。
原来Web中:
- http协议,无状态&短连接。
- 客户端主动连接服务端。
- 客户端向服务端发送消息,服务端接收到返回数据。
- 客户端接收到数据。
- 断开连接。
- https一些 + 对数据进行加密。
我们在开发过程中想要保留一些状态信息,基于Cookie来做。
现在支持:
- http协议,一次请求一次响应。
- websocket协议,创建连持久的连接不断开,基于这个连接可以进行收发数据。【服务端向客户端主动推送消息】
- web聊天室
- 实时图表,柱状图、饼图(Highcharts)
1.3.1 WebSocket原理
http协议
- 连接
- 数据传输
- 断开连接
websocket协议,是建立在http协议之上的。
连接,客户端发起。
握手(验证),客户端发送一个消息,后端接收到消息再做一些特殊处理并返回。 服务端支持websocket协议。
客户端向服务端发送
GET /chatsocket HTTP/1.1 Host: 127.0.0.1:8002 Connection: Upgrade Pragma: no-cache Cache-Control: no-cache Upgrade: websocket Origin: http://localhost:63342 Sec-WebSocket-Version: 13 Sec-WebSocket-Key: mnwFxiOlctXFN/DeMt1Amg== Sec-WebSocket-Extensions: permessage-deflate; client_max_window_bits ... ... \r\n\r\n服务端接收
mnwFxiOlctXFN/DeMt1Amg== 与 magic string 进行拼接。 magic string = "258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11" v1 = "mnwFxiOlctXFN/DeMt1Amg==" + "258EAFA5-E914-47DA-95CA-C5AB0DC85B11" v2 = hmac1(v1) v3 = base64(v2)HTTP/1.1 101 Switching Protocols Upgrade:websocket Connection: Upgrade Sec-WebSocket-Accept: 密文
收发数据(加密)
b"adasdjf;akjdfp;iujas;ldkjfpaisudflkasjd;fkjas;dkjf;aksjdf;ajksd;fjka;sdijkf"先获取第2个字节,8位。 10001010
再获取第二个字节的后7位。 0001010 -> payload len
- =127,2字节,8个字节, 其他字节(4字节 masking key + 数据)。
- =126,2字节,2个字节, 其他字节(4字节 masking key + 数据)。
- <=125,2字节, 其他字节(4字节 masking key + 数据)。
获取masking key,然后对数据进行解密
var DECODED = ""; for (var i = 0; i < ENCODED.length; i++) { DECODED[i] = ENCODED[i] ^ MASK[i % 4]; }
断开连接。
1.3.2 django框架
django默认不支持websocket,需要安装组件:
pip install channels配置:
注册channels
INSTALLED_APPS = [ 'django.contrib.admin', 'django.contrib.auth', 'django.contrib.contenttypes', 'django.contrib.sessions', 'django.contrib.messages', 'django.contrib.staticfiles', 'channels', ]
在settings.py中添加 asgi_application
ASGI_APPLICATION = "ws_demo.asgi.application"
修改asgi.py文件
import os from django.core.asgi import get_asgi_application from channels.routing import ProtocolTypeRouter, URLRouter from . import routing os.environ.setdefault('DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE', 'ws_demo.settings') # application = get_asgi_application() application = ProtocolTypeRouter({ "http": get_asgi_application(), "websocket": URLRouter(routing.websocket_urlpatterns), })
在settings.py的同级目录创建 routing.py
from django.urls import re_path
from app01 import consumers
websocket_urlpatterns = [
re_path(r'ws/(?P<group>\w+)/$', consumers.ChatConsumer.as_asgi()),
]
- 在app01目录下创建 consumers.py,编写处理处理websocket的业务逻辑。
from channels.generic.websocket import WebsocketConsumer
from channels.exceptions import StopConsumer
class ChatConsumer(WebsocketConsumer):
def websocket_connect(self, message):
# 有客户端来向后端发送websocket连接的请求时,自动触发。
# 服务端允许和客户端创建连接。
self.accept()
def websocket_receive(self, message):
# 浏览器基于websocket向后端发送数据,自动触发接收消息。
print(message)
self.send("不要回复不要回复")
# self.close()
def websocket_disconnect(self, message):
# 客户端与服务端断开连接时,自动触发。
print("断开连接")
raise StopConsumer()
在django中你要了解的:
urls.py
views.py
- websocket
routings.py
consumers.py
1.3.3 聊天室
访问地址看到聊天室的页面,http请求。
让客户端主动向服务端发起websocket连接,服务端接收到连接后通过(握手)。
客户端,websocket。
socket = new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:8000/room/123/");服务端
```python from channels.generic.websocket import WebsocketConsumer from channels.exceptions import StopConsumer
class ChatConsumer(WebsocketConsumer):
def websocket_connect(self, message):
print("有人来连接了...")
# 有客户端来向后端发送websocket连接的请求时,自动触发。
# 服务端允许和客户端创建连接(握手)。
self.accept()
```收发消息(客户端向服务端发消息)
客户端
<div> <input type="text" placeholder="请输入" id="txt"> <input type="button" value="发送" onclick="sendMessage()"> </div> <script> socket = new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:8000/room/123/"); function sendMessage() { let tag = document.getElementById("txt"); socket.send(tag.value); } </script>
服务端
```python from channels.generic.websocket import WebsocketConsumer from channels.exceptions import StopConsumer
class ChatConsumer(WebsocketConsumer):
def websocket_connect(self, message):
print("有人来连接了...")
# 有客户端来向后端发送websocket连接的请求时,自动触发。
# 服务端允许和客户端创建连接(握手)。
self.accept()
def websocket_receive(self, message):
# 浏览器基于websocket向后端发送数据,自动触发接收消息。
text = message['text'] # {'type': 'websocket.receive', 'text': '阿斯蒂芬'}
print("接收到消息-->", text)
```收发消息(服务端主动发给客户端)
服务端
```python from channels.generic.websocket import WebsocketConsumer from channels.exceptions import StopConsumer
class ChatConsumer(WebsocketConsumer):
def websocket_connect(self, message):
print("有人来连接了...")
# 有客户端来向后端发送websocket连接的请求时,自动触发。
# 服务端允许和客户端创建连接(握手)。
self.accept()
# 服务端给客户端发送消息
self.send("来了呀客官")
```客户端
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .message { height: 300px; border: 1px solid #dddddd; width: 100%; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="message" id="message"></div> <div> <input type="text" placeholder="请输入" id="txt"> <input type="button" value="发送" onclick="sendMessage()"> </div> <script> // http://www.baidu.com // ws://www.baidu.com socket = new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:8000/room/123/"); // 当websocket接收到服务端发来的消息时,自动会触发这个函数。 socket.onmessage = function (event) { console.log(event.data); } function sendMessage() { let tag = document.getElementById("txt"); socket.send(tag.value); } </script> </body> </html>
整合在一起:
前端:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
<style>
.message {
height: 300px;
border: 1px solid #dddddd;
width: 100%;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="message" id="message"></div>
<div>
<input type="text" placeholder="请输入" id="txt">
<input type="button" value="发送" onclick="sendMessage()">
<input type="button" value="关闭连接" onclick="closeConn()">
</div>
<script>
socket = new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:8000/room/123/");
// 创建好连接之后自动触发( 服务端执行self.accept() )
socket.onopen = function (event) {
let tag = document.createElement("div");
tag.innerText = "[连接成功]";
document.getElementById("message").appendChild(tag);
}
// 当websocket接收到服务端发来的消息时,自动会触发这个函数。
socket.onmessage = function (event) {
let tag = document.createElement("div");
tag.innerText = event.data;
document.getElementById("message").appendChild(tag);
}
// 服务端主动断开连接时,这个方法也被触发。
socket.onclose = function (event) {
let tag = document.createElement("div");
tag.innerText = "[断开连接]";
document.getElementById("message").appendChild(tag);
}
function sendMessage() {
let tag = document.getElementById("txt");
socket.send(tag.value);
}
function closeConn() {
socket.close(); // 向服务端发送断开连接的请求
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
from channels.generic.websocket import WebsocketConsumer
from channels.exceptions import StopConsumer
class ChatConsumer(WebsocketConsumer):
def websocket_connect(self, message):
print("有人来连接了...")
# 有客户端来向后端发送websocket连接的请求时,自动触发。
# 服务端允许和客户端创建连接(握手)。
self.accept()
# 服务端给客户端发送消息
# self.send("来了呀客官")
def websocket_receive(self, message):
# 浏览器基于websocket向后端发送数据,自动触发接收消息。
text = message['text'] # {'type': 'websocket.receive', 'text': '阿斯蒂芬'}
print("接收到消息-->", text)
if text == "关闭":
# 服务端主动关闭连接,给客户端发送一条断开连接的消息。
self.close()
# raise StopConsumer() # 如果服务端断开连接时,执行 StopConsumer异常,那么websocket_disconnect方法不再执行。
return
res = "{}SB".format(text)
self.send(res)
def websocket_disconnect(self, message):
print("断开连接了")
raise StopConsumer()
小结
基于django实现websocket请求,但只能对某个人进行处理。
1.3.4 群聊(一)
前端代码
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>Title</title> <style> .message { height: 300px; border: 1px solid #dddddd; width: 100%; } </style> </head> <body> <div class="message" id="message"></div> <div> <input type="text" placeholder="请输入" id="txt"> <input type="button" value="发送" onclick="sendMessage()"> <input type="button" value="关闭连接" onclick="closeConn()"> </div> <script> socket = new WebSocket("ws://127.0.0.1:8000/room/123/"); // 创建好连接之后自动触发( 服务端执行self.accept() ) socket.onopen = function (event) { let tag = document.createElement("div"); tag.innerText = "[连接成功]"; document.getElementById("message").appendChild(tag); } // 当websocket接收到服务端发来的消息时,自动会触发这个函数。 socket.onmessage = function (event) { let tag = document.createElement("div"); tag.innerText = event.data; document.getElementById("message").appendChild(tag); } // 服务端主动断开连接时,这个方法也被触发。 socket.onclose = function (event) { let tag = document.createElement("div"); tag.innerText = "[断开连接]"; document.getElementById("message").appendChild(tag); } function sendMessage() { let tag = document.getElementById("txt"); socket.send(tag.value); } function closeConn() { socket.close(); // 向服务端发送断开连接的请求 } </script> </body> </html>
后端
```python from channels.generic.websocket import WebsocketConsumer from channels.exceptions import StopConsumer
CONN_LIST = []
class ChatConsumer(WebsocketConsumer): def websocket_connect(self, message): print("有人来连接了...")
# 有客户端来向后端发送websocket连接的请求时,自动触发。
# 服务端允许和客户端创建连接(握手)。
self.accept()
CONN_LIST.append(self)
def websocket_receive(self, message):
# 浏览器基于websocket向后端发送数据,自动触发接收消息。
text = message['text'] # {'type': 'websocket.receive', 'text': '阿斯蒂芬'}
print("接收到消息-->", text)
res = "{}SB".format(text)
for conn in CONN_LIST:
conn.send(res)
def websocket_disconnect(self, message):
CONN_LIST.remove(self)
raise StopConsumer()#### 1.3.5 群聊(二)
基于channels中提供channel layers来实现。
- setting中配置。
```python
CHANNEL_LAYERS = {
"default": {
"BACKEND": "channels.layers.InMemoryChannelLayer",
}
}pip3 install channels-redisCHANNEL_LAYERS = {
"default": {
"BACKEND": "channels_redis.core.RedisChannelLayer",
"CONFIG": {
"hosts": [('10.211.55.25', 6379)]
},
},
}
consumers中特殊的代码。
```python from channels.generic.websocket import WebsocketConsumer from channels.exceptions import StopConsumer from asgiref.sync import async_to_sync
class ChatConsumer(WebsocketConsumer): def websocket_connect(self, message):
# 接收这个客户端的连接
self.accept()
# 获取群号,获取路由匹配中的
group = self.scope['url_route']['kwargs'].get("group")
# 将这个客户端的连接对象加入到某个地方(内存 or redis)
async_to_sync(self.channel_layer.group_add)(group, self.channel_name)
def websocket_receive(self, message):
group = self.scope['url_route']['kwargs'].get("group")
# 通知组内的所有客户端,执行 xx_oo 方法,在此方法中自己可以去定义任意的功能。
async_to_sync(self.channel_layer.group_send)(group, {"type": "xx.oo", 'message': message})
def xx_oo(self, event):
text = event['message']['text']
self.send(text)
def websocket_disconnect(self, message):
group = self.scope['url_route']['kwargs'].get("group")
async_to_sync(self.channel_layer.group_discard)(group, self.channel_name)
raise StopConsumer()### 总结
- websocket是什么?协议。
- django中实现websocket,channels组件。
- 单独连接和收发数据。
- 手动创建列表 & channel layers。
提醒:
- 运维&运维开发的同学,代码发布系统项目。(django 1.11.7讲)
- 工单系统
## 2.工单系统
### 2.1 前端gojs
```html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="myDiagramDiv" style="width:500px; height:350px; background-color: #DAE4E4;"></div>
<script src="gojs/go.js"></script>
<script>
var $ = go.GraphObject.make;
// 第一步:创建图表
var myDiagram = $(go.Diagram, "myDiagramDiv"); // 创建图表,用于在页面上画图
// 第二步:创建一个节点,内容为武沛齐
// $(go.TextBlock, {text: "武沛齐"}) 创建文本
var node = $(go.Node, $(go.TextBlock, {text: "武沛齐"}));
// 第三步:将节点添加到图表中
myDiagram.add(node);
</script>
</body>
</html><!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="myDiagramDiv" style="width:500px; height:350px; background-color: #DAE4E4;"></div>
<script src="gojs/go.js"></script>
<script>
var $ = go.GraphObject.make;
// 第一步:创建图表
var myDiagram = $(go.Diagram, "myDiagramDiv"); // 创建图表,用于在页面上画图
var node1 = $(go.Node, $(go.TextBlock, {text: "武沛齐"}));
myDiagram.add(node1);
var node2 = $(go.Node, $(go.TextBlock, {text: "武沛齐", stroke: 'red'}));
myDiagram.add(node2);
var node3 = $(go.Node, $(go.TextBlock, {text: "武沛齐", background: 'lightblue'}));
myDiagram.add(node3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="myDiagramDiv" style="width:500px; height:350px; background-color: #DAE4E4;"></div>
<script src="gojs/go.js"></script>
<script src="gojs/Figures.js"></script>
<script>
var $ = go.GraphObject.make;
var myDiagram = $(go.Diagram, "myDiagramDiv"); // 创建图表,用于在页面上画图
var node1 = $(go.Node,
$(go.Shape, {figure: "Ellipse", width: 40, height: 40})
);
myDiagram.add(node1);
var node2 = $(go.Node,
$(go.Shape, {figure: "RoundedRectangle", width: 40, height: 40, fill: 'green',stroke:'red'})
);
myDiagram.add(node2);
var node3 = $(go.Node,
$(go.Shape, {figure: "Rectangle", width: 40, height: 40, fill: null})
);
myDiagram.add(node3);
var node4 = $(go.Node,
$(go.Shape, {figure: "Diamond", width: 40, height: 40, fill: '#ddd'})
);
myDiagram.add(node4);
// 需要引入Figures.js
var node5 = $(go.Node,
$(go.Shape, {figure: "Club", width: 40, height: 40, fill: 'red'})
);
myDiagram.add(node5);
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="myDiagramDiv" style="width:500px; height:350px; background-color: #DAE4E4;"></div>
<script src="gojs/go.js"></script>
<script src="gojs/Figures.js"></script>
<script>
var $ = go.GraphObject.make;
var myDiagram = $(go.Diagram, "myDiagramDiv"); // 创建图表,用于在页面上画图
var node1 = $(go.Node,
"Vertical",
{
background: 'yellow',
padding: 8
},
$(go.Shape, {figure: "Ellipse", width: 40, height: 40}),
$(go.TextBlock, {text: "武沛齐"})
);
myDiagram.add(node1);
var node2 = $(go.Node,
"Horizontal",
{
background: 'white',
padding: 5
},
$(go.Shape, {figure: "RoundedRectangle", width: 40, height: 40}),
$(go.TextBlock, {text: "武沛齐"})
);
myDiagram.add(node2);
var node3 = $(go.Node,
"Auto",
$(go.Shape, {figure: "Ellipse", width: 80, height: 80, background: 'green', fill: 'red'}),
$(go.TextBlock, {text: "武沛齐"})
);
myDiagram.add(node3);
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="myDiagramDiv" style="width:800px; min-height:450px; background-color: #DAE4E4;"></div>
<script src="gojs/go-debug.js"></script>
<script>
var $ = go.GraphObject.make;
var myDiagram = $(go.Diagram, "myDiagramDiv",
{layout: $(go.TreeLayout, {angle: 0})}
); // 创建图表,用于在页面上画图
var startNode = $(go.Node, "Auto",
$(go.Shape, {figure: "Ellipse", width: 40, height: 40, fill: '#79C900', stroke: '#79C900'}),
$(go.TextBlock, {text: '开始', stroke: 'white'})
);
myDiagram.add(startNode);
var downloadNode = $(go.Node, "Auto",
$(go.Shape, {figure: "RoundedRectangle", height: 40, fill: '#79C900', stroke: '#79C900'}),
$(go.TextBlock, {text: '下载代码', stroke: 'white'})
);
myDiagram.add(downloadNode);
var startToDownloadLink = $(go.Link,
{fromNode: startNode, toNode: downloadNode},
$(go.Shape, {strokeWidth: 1}),
$(go.Shape, {toArrow: "OpenTriangle", fill: null, strokeWidth: 1})
);
myDiagram.add(startToDownloadLink);
var zipNode = $(go.Node, "Auto",
$(go.Shape, {figure: "RoundedRectangle", height: 40, fill: '#79C900', stroke: '#79C900'}),
$(go.TextBlock, {text: '本地打包', stroke: 'white'})
);
myDiagram.add(zipNode);
var downloadToZipLink = $(go.Link,
{fromNode: downloadNode, toNode: zipNode},
$(go.Shape, {strokeWidth: 1}),
$(go.Shape, {toArrow: "OpenTriangle", fill: null, strokeWidth: 1})
);
myDiagram.add(downloadToZipLink);
for (var i = 1; i < 6; i++) {
var node = $(go.Node, "Auto",
$(go.Shape, {figure: "RoundedRectangle", height: 40, fill: 'lightgray', stroke: 'lightgray'}),
$(go.TextBlock, {text: '服务器' + i, stroke: 'white', margin: 5})
);
myDiagram.add(node);
var nodeToZipLink = $(go.Link,
{fromNode: zipNode, toNode: node, routing: go.Link.Orthogonal},
$(go.Shape, {strokeWidth: 1, stroke: 'lightgray'}),
$(go.Shape, {toArrow: "OpenTriangle", fill: null, strokeWidth: 1, stroke: 'lightgray'})
);
myDiagram.add(nodeToZipLink);
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="diagramDiv" style="width:100%; min-height:450px; background-color: #DAE4E4;"></div>
<script src="gojs/go-no-logo.js"></script>
<script>
var $ = go.GraphObject.make;
var diagram = $(go.Diagram, "diagramDiv", {
layout: $(go.TreeLayout, {
angle: 0,
nodeSpacing: 20,
layerSpacing: 70
})
});
// 节点的模板
diagram.nodeTemplate = $(go.Node, "Auto",
$(go.Shape, {
figure: "RoundedRectangle",
fill: 'lightgray',
stroke: 'lightgray'
}, new go.Binding("figure", "figure"), new go.Binding("fill", "color"), new go.Binding("stroke", "color")),
$(go.TextBlock, {margin: 8}, new go.Binding("text", "text"))
);
// 连接的模板
diagram.linkTemplate = $(go.Link,
{routing: go.Link.Orthogonal},
$(go.Shape, {stroke: 'lightgray'}, new go.Binding('stroke', 'link_color')),
$(go.Shape, {toArrow: "OpenTriangle", stroke: 'lightgray'}, new go.Binding('stroke', 'link_color')),
$(go.TextBlock, {font: '8pt serif', segmentOffset: new go.Point(0, -10)}, new go.Binding("text", "link_text"))
);
var nodeDataArray = [
{key: "start", text: '开始', figure: 'Ellipse', color: "lightgreen"},
{key: "download", parent: 'start', text: '下载代码', color: "lightgreen", link_text: '执行中...'},
{key: "compile", parent: 'download', text: '本地编译', color: "lightgreen"},
{key: "zip", parent: 'compile', text: '打包', color: "red", link_color: 'red'},
{key: "c1", text: '服务器1', parent: "zip"},
{key: "c11", text: '服务重启', parent: "c1",color: "lightgrey"},
{key: "c2", text: '服务器2', parent: "zip"},
{key: "c21", text: '服务重启', parent: "c2"},
{key: "c3", text: '服务器3', parent: "zip"},
{key: "c31", text: '服务重启', parent: "c3"},
];
diagram.model = new go.TreeModel(nodeDataArray);
/*
diagram.model.addNodeData({key: "c4", text: '服务器3', parent: "c3", color: "lightgreen"})
var c1 = diagram.model.findNodeDataForKey("c1");
diagram.model.setDataProperty(c1, "color", "red");
diagram.model.setDataProperty(c1, "link_text", "执行中...");
diagram.model.setDataProperty(c1, "link_color", "red");
*/
</script>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="diagramDiv" style="width:100%; min-height:450px; background-color: #DAE4E4;"></div>
<script src="gojs/go-no-logo.js"></script>
<script>
var $ = go.GraphObject.make;
var diagram = $(go.Diagram, "diagramDiv", {
layout: $(go.TreeLayout, {
angle: 0,
nodeSpacing: 20,
layerSpacing: 70
})
});
// 节点
var nodeDataArray = [
{key: "Alpha"},
{key: "Beta"},
{key: "papa"},
{key: "bilibili"}
];
// 关系
var linkDataArray = [
{from: "Alpha", to: "Beta"},
{from: "Alpha", to: "papa"},
{from: "Beta", to: "bilibili"},
{from: "papa", to: "bilibili"},
];
diagram.model = new go.GraphLinksModel(nodeDataArray, linkDataArray);
diagram.model.addNodeData({key: "c4", text: '服务器3', color: "lightgreen"})
diagram.model.addLinkData({from: "bilibili", to: 'c4'})
</script>
</body>
</html>
2.2 后端django + websocket
- 表结构
- websocket+gojs
- 流程图标 + go.js
- 同意 or 不同意
总结
websocket原理
websocket实现的功能(django中channels的应用)
gojs
class A(models.Model):
title = ...
class B(models.Model):
name = ...
a1 = models.ForeignKey(to=A,related_name='x')
obj = modes.B.objects.filter(id=1).first()
obj.a1.title
abj = models.A.objects.filter(id=2).first()
abj.x.all()